Top 5 Internet Explorer issues:-
Issues viewing Web pages
i) "Page cannot be displayed" errors
ii) Red x instead of pictures
iii) View, Source doesn't work
To address the issues above, you may need to try one, some, or all of the following three procedures.
Empty the cache
The first thing to do when Internet Explorer is misbehaving is empty your Internet Explorer cache. Often the cache is not corrupt or damaged – it is simply too large.
1. Click Tools, then Internet Options, and then click the Delete Files button.
2. A Delete Files window will appear. Select the option to Delete all offline content, and then click OK.
3. Click Settings and reduce the size of your cache to, say, 50 to 100 MB (more if you routinely download very large files).
This will invariably fix the dreaded red x, View, Source, and sometimes "Page cannot be displayed" errors.
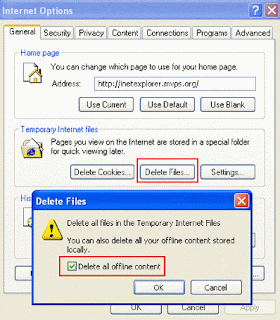 Troubleshooting fix number 1—empty your IE cache.
Troubleshooting fix number 1—empty your IE cache.Emptying the cache will not be sufficient to fix things if a hidden file in the cache folders, called index.dat, is corrupt. Our best alternative in such a situation is to delete the cache folders in their entirety, but this cannot be done from within Windows under normal circumstances.
Index.dat is a system file, and any attempt to delete it while Windows is running or while the user is logged on will be blocked. Therefore, we need to reboot into DOS mode or, when running later versions of Windows that support user accounts, we need to log in to Windows using a different Administrator account to that which is affected.
Note: The following procedure is for advanced users.
If you are running Windows 95, Windows 98, or Windows Millennium Edition (Me)
1. Click on Start, then Shut Down, and select the Restart the Computer in MS-DOS mode option. (If you are running Windows Me use a Windows 98 startup disc to access DOS mode.)
The steps required to create a startup disk are the same for Windows 95, Windows 98, and Windows Me.
1. Click on Start, point to Settings, and then click on Control Panel.
2. Open Add/Remove Programs, click on the Startup Disk tab, and then click Create Disk and follow the prompts. Make sure you have an empty floppy disk ready.
If you have difficulties when using Add/Remove Programs to create a startup disk (for example, if the Wizard prompts for your operating system installation disk and you cannot find it, or you only have a manufacturer provided restore disk or partition) go to www.bootdisk.com/bootdisk.htm. Download a Windows98 boot disk executable file from that site, put an empty floppy disk in the correct disk drive, and then double click on the downloaded file to make the disk. I recommend Windows 98 SE Custom, which includes smartdrv.
Turn your PC off, and place the startup disk in the computer’s floppy drive. Turn on your PC, which should read the startup disk and load the DOS operating system instead of Windows.
Once the system has finished booting into DOS mode, run the following commands from the Windows directory, typically displayed in DOS as c:\windows\>.
smartdrv
deltree tempor~1
Just to be sure, let's also run:
deltree history
deltree cookies
I should explain what tempor~1 means. The version of DOS that is included on the Windows 98 startup disk does not support long file or folder names like "temporary internet files." We are restricted to 8 letters only. Therefore, any file or folder which has more than eight letters to its name must shortened, and appended with ~1 when use the Windows 98 version of DOS.
If you are running Windows 2000 or Windows XP
We do things differently when working with operating systems that support User Accounts, such as Windows 2000 and Windows XP. Firstly, Windows 98 boot disks do not work if a hard drive is formatted as NTFS instead of FAT . Secondly, Windows 2000 and Windows XP use a more complicated directory structure than Windows 95 and Windows 98, making DOS more difficult to use successfully.
The path to the Internet Explorer cache directory will typically be something similar to:
C:\Documents and Settings\username\Local Settings\Temporary Internet Files\...
Thankfully, Windows 2000 and Windows XP users can log in using an Administrator account to delete the folders in question directly from within Windows Explorer. Note that an Administrator cannot delete his own Internet Explorer cache folders. He must log on using a different Administrator account.
Edit the HOST file
Note: The following procedure is for advanced users.
The HOSTS file is a hidden file used by some Internet related programs to control Web browsing by directly linking particular Web sites to pre-set IP addresses. The only problem is, if a Web page's IP address changes, the HOSTS file will not update itself to suit, causing "Page cannot be displayed" errors.
The HOSTS file can be viewed and edited using Notepad, but first we must temporarily show hidden files.
For Windows XP
1. Click Start, and then click Control Panel.
2. Click Appearance and Themes, and then click Folder Options.
For older systems
1. Double-click My Computer, click View, and then click Folder Options.
2. On the View tab, under Hidden files and folders, click Show hidden files and folders, and then clear the Hide protected operating system files check box.
Find and edit your HOSTS file
The correct directory for a HOSTS file depends on what version of Windows you are running:
Windows XP = C:\Windows\System32\Drivers\Etc
Windows 2K = C:\Winnt\System32\Drivers\Etc
Win 98\ME = C:\Windows
Once you have found your HOSTS file, right-click on the HOSTS file, and then select Open. You will be asked to choose a program to use. Select Notepad, but make sure you that you do NOT turn on any option to always use the same program.
Examine the content of your HOSTS file, and compare it to the screenshot below. We do not need to worry about any line that begins with an # because is ignored by Windows. Also, the line "127.0.0.1 localhost" can be safely ignored, because it is a standard entry.
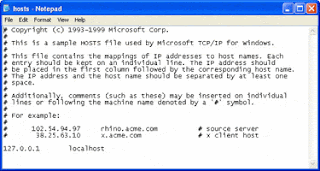
A HOSTS file can be used to control Web page to IP address associations
Anything else that appears in your HOSTS file without an # at the beginning, apart from the "127.0.0.1 localhost" line, should be viewed with suspicion when we are trying to diagnose the cause of "Page cannot be displayed" errors. The quickest way to test for HOSTS file involvement is to right click the HOSTS file, then select Rename. Add the letter X to the beginning or end of the file name and then ok your changes. By changing the name of the HOSTS file, we stop Internet Explorer from using it, and therefore resolve any issues caused by the file.
Repair Layered Service Provider problems
Sometimes Internet Explorer is unable to access the Internet if software known as Layered Service Provider (LSP) has been removed incorrectly from a computer. You might not know you have this software; it is sometimes installed by unrelated software such as file-sharing programs, without your knowledge. In such cases, you will need to run LSPfix or Winsockxpfix. As its name suggests, Winsockxpfix should only be used on machines running Windows XP. LSPfix can be used on all other consumer versions of Windows, but make sure that Winsock 2 has been installed on Windows 95 machines.
Issues related to default browser settings
iv) Error messages when attempting to send a page or link by e-mail
First, reset your default e-mail client from within Internet Explorer. To do this go to Tools, then Internet Options, then Programs, then select your e-mail program of choice.
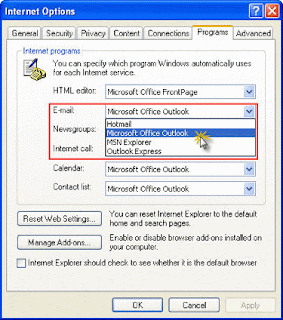
The easiest way to set your default e-mail client is from within Internet Explorer
Sometimes your e-mail program will not appear in the drop down list shown above. When this happens, we need to re-register the program in question.
To re-register your e-mail program:
1. Click Start, then click Run, and then type the appropriate command based on the following e-mail programs:
Outlook Express:
"C:\Program Files\Outlook Express\Msimn.Exe" /reg
Outlook:
"c:\program files\microsoft office\office\outlook.exe" /checkclient
Make sure the path to msimn.exe or outlook.exe is correct for your machine. Type the command line exactly as it appears, including quote marks and spaces.
If using a non-Microsoft e-mail program:
A program must be Internet Explorer aware to automatically list itself as a default program option. If the program does not appear, there are a couple of things you can do. First, you can right-click the executable file for the program, and see if Register appears as an option, (which should cause the program to be listed on the drop box on the Program Tab)
Otherwise, there's a manual method, but it involves editing the registry and adding the program under:
HKEY LOCAL MACHINE\Software\Clients\mail
-or-
HKEY LOCAL MACHINE\Software\Clients\news
You will need to contact your program's vendor for the appropriate syntax.
V) Internet Explorer freezes, shuts down without warning, or the computer reboots.
This problem is often caused by out-of-date video drivers. Go to the Web site run by the manufacturer of your video card and download, then install, the latest (non-beta) drivers for your video card.
Alternatively, you can try the following:
1. Click Start, and then click Control Panel.
2. Click Display (in classic view of Windows XP), click the Settings tab, and then click Advanced.
3. Click the Performance or Troubleshooting tab (depending on your operating system), and then reduce hardware acceleration a notch at a time until your system stabilizes.
source:- http://www.microsoft.com/windows/ie/community/columns/ietopten.mspx#top

1 comment:
tere bhen ka bhosda chodu madar chood bhen ki lode randi ki auladh bhosde ke sale///////////tere bhen ki chut
Post a Comment